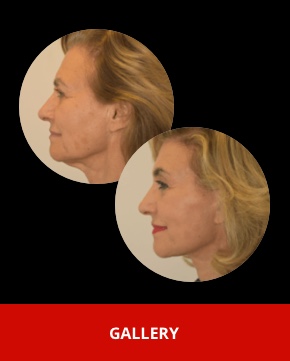
Lower blepharoplasty
Lower blepharoplasty, also known as lower eyelid surgery, is a cosmetic procedure designed to improve the appearance of the lower eyelids. It addresses issues such as puffiness, bags under the eyes, excess skin, and fine wrinkles. Here is a detailed description of the procedure:
Indications
- Puffiness and Bags: Caused by fat deposits that create a tired or aged appearance.
- Excess Skin and Wrinkles: Loose skin and fine wrinkles around the lower eyelids.
- Functional Concerns: In some cases, to improve vision or comfort by removing obstructive tissues.
Preoperative Assessment
- Consultation:
- Detailed discussion of the patient’s goals and expectations.
- Comprehensive medical history review, including any previous eye surgeries, medical conditions, medications, and allergies.
- Physical examination of the eyes and eyelids, including skin quality, muscle tone, and fat deposits.
- Photography:
- Preoperative photographs are taken for planning and comparison of postoperative results.
- Discussion of Risks and Benefits:
- Explanation of potential risks, benefits, and realistic outcomes of the surgery.
- Review of the patient’s medical history and discussion of any specific concerns.
Anesthesia
- Local Anesthesia with Sedation: Commonly used to numb the surgical area while the patient remains relaxed and comfortable.
- General Anesthesia: In some cases, general anesthesia may be preferred based on patient and surgeon preference.
Surgical Procedure
Approaches
- Transconjunctival Approach:
- Ideal for younger patients with good skin elasticity and primarily fat-related issues.
- Incision is made on the inside of the lower eyelid (conjunctiva), leaving no visible external scar.
- Provides access to remove or reposition fat deposits.
- Transcutaneous Approach:
- Preferred when there is significant excess skin or muscle laxity.
- Incision is made just below the lower lash line, extending slightly beyond the outer corner.
- Allows for removal of excess skin, muscle tightening, and fat modification.
Steps of the Procedure
- Incision:
- Transconjunctival: Incision made inside the lower eyelid.
- Transcutaneous: Incision made just below the lash line.
- Fat Removal or Repositioning:
- Fat Removal: Excess fat that causes puffiness is carefully removed.
- Fat Repositioning: Fat may be redistributed to fill hollow areas and create a smoother contour, reducing the appearance of tear troughs and hollow eyes.
- Skin and Muscle Modification:
- Excess Skin Removal: Loose or sagging skin is excised.
- Muscle Tightening: Orbicularis oculi muscle may be tightened or repositioned to improve support and contour.
- Re-draping and Closure:
- Re-draping: Skin and tissues are gently re-draped to create a smooth, natural look.
- Closure: Incisions are closed with fine sutures. For the transcutaneous approach, sutures are typically placed just below the lash line to minimize visible scarring.
- Additional Techniques:
- Laser Resurfacing or Chemical Peels: Sometimes used in conjunction to improve skin texture and reduce fine wrinkles.
- Canthopexy or Canthoplasty: Procedures to tighten and support the outer corner of the eyelid if needed.
Postoperative Care
- Immediate Postoperative Care:
- Monitoring in the recovery area until the effects of anaesthesia wear off.
- Application of cold compresses to reduce swelling and bruising.
- Instructions:
- Detailed postoperative care instructions, including how to clean the eyes, apply prescribed ointments, and manage pain with medications.
- Avoiding strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and bending over for at least a week.
- Keeping the head elevated to minimise swelling.
- Follow-Up Visits:
- Scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing, remove sutures (if non-absorbable sutures are used), and address any complications.
- Recovery Timeline:
- Initial swelling and bruising typically subside within 1-2 weeks.
- Most patients can return to normal activities within 7-10 days, but should avoid strenuous activities and contact lenses for a few weeks.
Expected Results
- Immediate Effects:
- Initial results are visible once swelling and bruising diminish, usually within a few weeks.
- Final Outcome:
- Full results become more apparent after a few months as tissues settle and incision lines fade.
- Patients can expect a more youthful and refreshed appearance with smoother lower eyelids and reduced puffiness.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Common Risks:
- Swelling and bruising
- Temporary discomfort and dry eyes
- Itching or sensitivity to light
- Rare Complications:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Asymmetry
- Changes in sensation
- Ectropion (outward turning of the eyelid)
- Difficulty closing the eyes (lagophthalmos)
- Managing Complications:
- Most complications can be managed with appropriate medical care and follow-up visits.
- Severe complications are rare but may require additional surgical intervention.
Advantages
- Aesthetic Improvement:
- Provides a more youthful and refreshed appearance, reducing signs of aging and fatigue.
- Functional Improvement:
- Can improve vision if excess skin obstructs the visual field.
- Minimal Scarring:
- For the transconjunctival approach, there are no external scars. For the transcutaneous approach, scars are well-concealed within the natural eyelid contours and tend to fade over time.
Conclusion
Lower blepharoplasty is a highly effective procedure for improving both the function and appearance of the lower eyelids. With proper surgical technique and postoperative care, patients can achieve significant rejuvenation of the eye area, resulting in a more youthful and refreshed look.