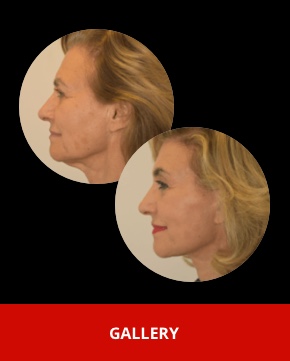
Upper blepharoplasty
Upper blepharoplasty, also known as upper eyelid surgery, is a cosmetic procedure designed to remove excess skin, muscle, and sometimes fat from the upper eyelids. This surgery aims to improve the appearance of the upper eyelids and can also enhance vision if sagging skin obstructs the visual field. Here’s a detailed description of the procedure:
Indications
- Excess Upper Eyelid Skin: Sagging or drooping skin that affects the natural contour of the upper eyelid.
- Impaired Vision: Overhanging skin that obstructs peripheral vision.
- Eyelid Puffiness: Swollen or puffy upper eyelids due to fat deposits.
- Aesthetic Improvement: Desire for a more youthful and refreshed appearance.
Preoperative Assessment
- Consultation:
- Detailed medical history and discussion of patient’s goals and expectations.
- Physical examination of the eyes and eyelids, assessing skin elasticity, muscle tone, and fat deposits.
- Evaluation of tear production and eye health to rule out conditions like dry eye.
- Photography:
- Preoperative photographs are taken for surgical planning and to compare postoperative results.
- Discussion of Risks and Benefits:
- Explanation of potential risks, benefits, and realistic outcomes of the surgery.
- Review of the patient’s medical history, including any medications, allergies, or previous surgeries.
Anaesthesia
- Local Anesthesia with Sedation: Commonly used to numb the surgical area while the patient remains relaxed and comfortable.
- General Anesthesia: In some cases, general anesthesia may be preferred based on patient and surgeon preference.
Surgical Procedure
- Marking the Incision:
- The surgeon marks the natural crease of the upper eyelid to determine the incision line. This ensures that the scar will be hidden within the natural fold of the eyelid.
- Making the Incision:
- An incision is made along the marked lines in the natural crease of the upper eyelid, extending slightly beyond the outer corner to address any lateral hooding.
- The incision is carefully planned to follow the natural lines and folds of the eyelid for minimal visible scarring.
- Removal of Excess Tissue:
- Skin: Excess skin is excised to eliminate the droopy appearance.
- Muscle: A strip of the underlying orbicularis oculi muscle may be removed to enhance the eyelid contour.
- Fat: Protruding fat pockets, often found in the inner part of the upper eyelid, may be removed or repositioned to reduce puffiness.
- Repositioning:
- In some cases, fat may be repositioned rather than removed to avoid a hollowed appearance and to maintain a natural look.
- Closure:
- The incision is closed with fine sutures, usually 6-0 or 7-0 nylon or absorbable sutures.
- The surgeon may use tissue adhesives to minimize scarring and promote better healing.
- Skin glue or adhesive strips might be applied to support the incision during the initial healing period.
Postoperative Care
- Immediate Postoperative Care:
- The patient is monitored in the recovery area until the effects of anesthesia wear off.
- Cold compresses are applied to reduce swelling and bruising.
- Instructions:
- Detailed postoperative care instructions are provided, including how to clean the eyes, apply prescribed ointments, and manage pain with medications.
- The patient is advised to keep their head elevated and avoid strenuous activities for the first few days.
- Follow-Up Visits:
- Scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing, remove sutures (if non-absorbable sutures are used), and address any complications.
- Recovery Timeline:
- Swelling and bruising typically subside within 1-2 weeks.
- Most patients can return to normal activities within 7-10 days, but should avoid strenuous activities and contact lenses for a few weeks.
Expected Results
- Immediate Effects:
- Initial results are visible once swelling and bruising diminish, usually within a few weeks.
- Final Outcome:
- The final results become more apparent after a few months as tissues settle and the incision lines fade.
- Patients can expect a more youthful and alert appearance with a smooth upper eyelid contour.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Common Risks:
- Swelling and bruising
- Temporary discomfort and dry eyes
- Itching or sensitivity to light
- Rare Complications:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Asymmetry
- Changes in sensation
- Difficulty closing the eyes (lagophthalmos)
- Managing Complications:
- Most complications can be managed with appropriate medical care and follow-up visits.
- Severe complications are rare but may require additional surgical intervention.
Advantages
- Functional Improvement:
- Can significantly improve vision if excess skin obstructs the visual field.
- Aesthetic Enhancement:
- Provides a more youthful and refreshed appearance, reducing signs of aging and fatigue.
- Minimal Scarring:
- Scars are well-concealed within the natural eyelid creases and tend to fade over time.
Conclusion
Upper blepharoplasty is a highly effective procedure for improving both the function and appearance of the upper eyelids. With proper surgical technique and postoperative care, patients can achieve significant rejuvenation of the eye area, resulting in a more youthful and alert look.